-
木香为菊科风毛菊属药用植物木香(Saussurea costus (Falc.) Lipech.)的干燥根,具有健脾和胃、调气解郁、止痛、安胎之功效,为我国传统常用中药材,主产于我国四川、重庆、云南等地区[1].近年来,由于人工栽培面积不断扩大,木香的病害愈发严重,尤其是根腐病对木香的产量和品质影响较大.该病常由土壤中的尖孢镰刀菌(Fusarium oxysporum)引起,7~8月发病严重.木香感病时,根部或茎基部出现暗褐色损伤,地上部叶色暗淡、叶片萎蔫.为害较重时根部逐渐腐烂、变黑,地上部分枯萎死亡.在高温多雨、田间排水不良的情况下极易发生且为害较重.该种病害常大面积发生,造成木香大量减产,严重威胁木香生产,造成巨大的经济损失[2].目前,生产上常采取的防治措施多为药剂喷施,不可避免地带来农药残留、环境污染以及抗药性等问题[3].实践证明,生物防治是有效替代化学防控的可行方案之一,已经受到人们的重视[4].本研究旨在从木香植株根际土壤中筛选出高效的生防细菌,并对其抑菌作用进行初步研究,以期为木香根腐病安全有效的生物防治提供依据.
全文HTML
-
供试土样采自重庆南川茶沙坝木香种植区,采集与发病植株相邻的健康木香植株的根际土壤作为细菌分离土样.
供试木香根腐病菌——尖孢镰刀菌(Fusarium oxysporum)由本实验室保存.
供试培养基包括NA培养基:牛肉浸膏3 g,蛋白胨5 g,葡萄糖2.5 g,琼脂18 g,蒸馏水1 000 mL,pH值(7.0±0.1);PDA培养基:马铃薯200 g,葡萄糖20 g,琼脂15 g,蒸馏水1 000 mL;LB培养基:胰化蛋白胨10 g,氯化钠10 g,酵母提取物5 g,琼脂15 g,蒸馏水1 000 mL.
-
称取5 g根际土壤样品,溶于45 mL无菌水的三角瓶中,在摇床上充分震荡30 min,制成土壤悬浮液,静置后,在无菌条件下取1 mL上清液逐级稀释,依次获得各质量浓度梯度的菌悬液.分别取1 mg/mL,0.1 mg/mL和0.01 mg/mL 3个稀释梯度的土壤悬浮液100 μL涂布于NA培养基平板上,每个浓度梯度3个重复,37 ℃倒置培养24 h.分离纯化细菌3~5次,将纯化后的菌株用甘油保存法-80 ℃保存备用.
-
初筛:将尖孢镰刀菌接种于PDA斜面,25 ℃培养3~4 d,加入灭菌的无菌水,刮下孢子,充分震荡混匀,用无菌脱脂棉过滤,稀释制成约1×107 cfu/mL孢子的菌悬液.取500 μL孢子悬液加入到100 mL融化冷却至45 ℃左右的PDA培养基中,摇匀,倒入灭菌培养皿中,制成含病原菌的琼脂平板.在病原菌平板上用“十字”划线法接入待检测的细菌菌株,28 ℃恒温培养48 h后观察结果[5].挑选出对木香根腐病菌有明显拮抗作用的细菌进行复筛.
复筛:采用平板对峙法进行复筛,在PDA平板中央接种木香根腐病原菌菌盘(直径5 mm),四周等距离2.5 cm处接入待测菌株,空白对照不接筛选菌. 28 ℃恒温培养,每个处理重复3次. 5 d后,统计其对木香根腐病原菌的抑菌率.
其中:IR表示抑菌率,a表示对照菌落的直径,b表示处理组菌落的直径.
-
切取活化后的木香根腐病原菌菌饼(直径6 mm)接入极薄的PDA平板中央,在其四周等距离2.5 cm处分别接入拮抗细菌,以不接入拮抗菌的菌丝为对照,25 ℃培养5 d,然后挑取对峙界面处的病原菌菌丝制成涂片,经乳酸酚棉蓝染色后,置于显微镜下观察并拍照[6].
-
1) 菌株形态学观察.将筛选到的拮抗菌株接种到NA平板上,28 ℃培养24 h,观察菌落形态.包括菌落大小、表面特征、边缘形态、润湿程度、挑起难易、颜色、是否产色素、正面和反面情况、与培养基结合紧密程度等.然后挑取NA平板上少许菌株经革兰氏染色及芽孢染色,在光学显微镜下观察菌体及芽孢的形态.
2) 菌株生理生化特性测试.参考《常见细菌系统鉴定手册》[7]和《伯杰细菌鉴定手册》[8]的方法,对拮抗菌株进行革兰氏染色、耐盐性检测、接触酶反应、硝酸盐还原反应、V-P反应、柠檬酸盐利用、最适生长温度测定、碳水化合物利用及淀粉水解等生理生化特性进行测试.
3) 拮抗菌株的16S rDNA基因序列分析[9].模板:拮抗细菌基因组DNA.引物:正向引物为27F:5'-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3',反向物为1495R:5'-TACGGCTACCTTGTTACGA-3'. PCR体系:DNA(70 ng/μL)模板2 μL;dNTP Mixture(2.5 mmol/L)2.5 μL;引物(20 μmol/L)各1.5 μL;Extaq DNA聚合酶0.2 μL;10×Extaq Buffer(Mg2+pluse)5 μL;补足ddH2O到50 μL. PCR条件:预变性94 ℃ 3 min;94 ℃变性1 min,55 ℃退火1 min,72 ℃延伸3 min,共30个循环;最后72 ℃延伸5 min. PCR产物经纯化后,送上海生工生物工程技术服务有限公司测序.将所测得的16S rDNA序列用BLAST软件与GenBank数据库进行相似性比对,应用Clustal X[10]进行多重比对后,根据MEGA 5.0软件采用Neibor-Joining方法构建系统发育树.
1.1. 试验材料
1.2. 试验方法
1.2.1. 根际土壤细菌的分离纯化
1.2.2. 木香根腐病拮抗细菌的筛选
1.2.3. 拮抗菌株对病原菌菌丝生长的影响
1.2.4. 拮抗细菌的鉴定
-
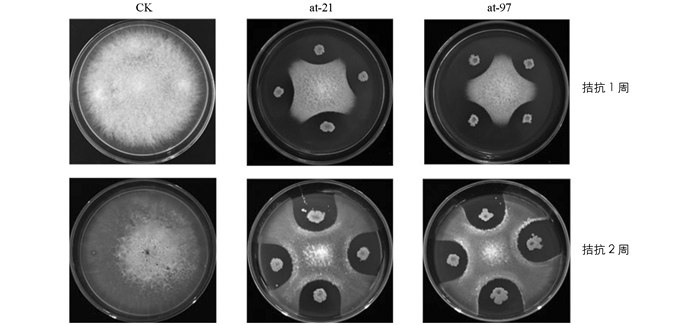
从根际土壤中共分离得到细菌324株,通过室内对峙培养,共筛选到12株对木香根腐病菌有较强拮抗活性的菌株,其中菌株at-21和at-97的抑制作用较为明显.经测定抑菌带宽度分别为5.2 mm和5.5 mm,抑菌率分别为68.8%和76.6%,与其他处理间差异具有统计学意义(p<0.05)(图 1).结果显示,病原菌与拮抗菌之间可形成明显的抑菌带,且抑菌带宽度不随时间的推移而显著改变,表明拮抗细菌at-21和at-97对木香根腐病原菌有较好的拮抗抑制效果.
-
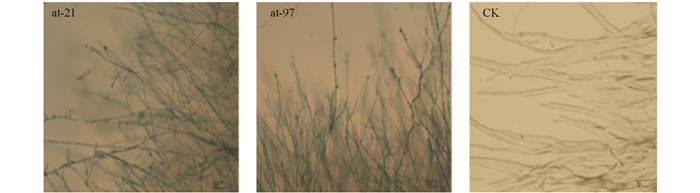
在光学显微镜下观察了拮抗细菌at-21和at-97对病原菌菌丝生长的影响,结果显示被抑制的菌丝生长畸形、菌丝变短,分岔增多,而正常菌丝生长均匀,表面光滑而舒展(图 2),说明病原菌菌丝在拮抗细菌的作用下,生长受到了明显的抑制.
-
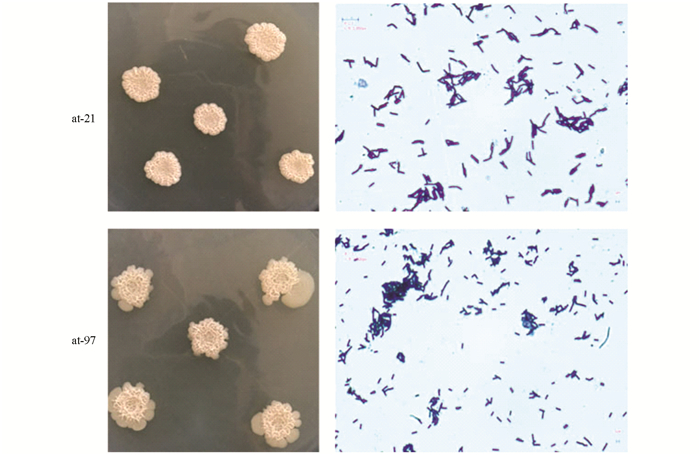
菌株at-21和at-97在NA培养基平板上30 ℃培养20 h的菌落形态如图 3所示.菌落形态近圆形,乳白色或微黄色,边缘湿润且不整齐,表面皱褶干燥.经乳酸酚棉蓝染色后置于显微镜下观察,菌体成线状排列,单个菌体呈杆状,宽约0.8 μm,长约2.5 μm,有芽孢,芽孢呈椭圆形中生,稍膨大,长约1.6 μm,宽约0.7 μm,革兰氏染色呈阳性,具有典型的芽孢杆菌特征.
-
2个菌株可在20~35 ℃的温度下生长,其最适生长温度为30 ℃,能氧化利用葡萄糖、D-果糖、蔗糖和乳糖,可以利用牛肉膏、胰化蛋白胨、硝酸铵、硫酸铵、酵母膏,接触酶反应、V-P反应呈阳性,硝酸盐还原反应生成红色化合物,能利用柠檬酸盐,可以水解淀粉,在含1%~7%的NaCl液体培养基中均能生长,说明两个菌株的生理生化特性与芽孢杆菌属菌的各项指标较为接近(表 1).
-
经16S rDNA测序分析,扩增后的菌株at-21和at-97的序列长度分别为1 421 bp和1 403 bp,将测得的序列通过BLAST程序与Genbank中序列进行比对分析,结果显示菌株at-21和at-97与芽孢杆菌属同源,相似度高达100%.采用Clustal X软件与Genbank中的相似序列进行多重序列比对,再用MEGA 6.0构建系统进化树.结果表明(图 4),菌株at-21与Bacillussp sp. strain ADG2(登录号:MF509828.1)最为相似,而at-97与菌株Bacillus subtilis strain IAM 12118(登录号:NR112116.2)的同源相似性最高.因此,综合菌株的形态特征、生理生化特征及分子生物学鉴定,拮抗菌株at-21鉴定为贝莱斯芽孢杆菌,菌株at-97鉴定为枯草芽孢杆菌.
2.1. 拮抗细菌的分离和筛选
2.2. 拮抗细菌对木香根腐病原菌菌丝生长的抑制作用
2.3. 拮抗菌株的鉴定
2.3.1. 菌体形态
2.3.2. 菌株生理生化特征
2.3.3. 拮抗细菌的16S rDNA序列分析
-
土传病害一直是困扰中药材生产的难点问题,尤其是镰刀菌引起的根腐病,是中草药生长过程中一类常见的毁灭性土传病害,素有“植物癌症”之称[11].因此,对中药材根腐病进行有效防控,是保障其可持续发展的重要环节.利用拮抗微生物防治中药材根腐病在拮抗菌株的筛选、作用机制及田间防效等方面取得了诸多成绩,有利于保持生态平衡,符合中药材规范化种植的要求,具有广阔的发展前景[12].本研究采用平板对峙培养法,从木香根腐病发病严重地块的健康植株根际土壤中筛选得到两株对木香根腐病原菌有较好拮抗作用的细菌菌株at-21和at-97,通过多次试验表明,其抑菌效果稳定.综合菌株的形态特征、生理生化特征及分子生物学鉴定结果,菌株at-21鉴定为贝莱斯芽孢杆菌,菌株at-97鉴定为枯草芽孢杆菌.本研究利用相对抑菌值来筛选拮抗菌株,而平板对峙培养的防效与田间防效未必相同,因而下一步计划开展拮抗菌株的盆栽及田间试验测试其应用防效,并对其抑菌机制进行初步探索.



 下载:
下载: