-
开放科学(资源服务)标志码(OSID):

-
犬弓首蛔虫Toxocara canis是一种寄生在犬及犬科动物小肠内的寄生虫,其感染性虫卵或幼虫是弓首蛔虫病(Toxocariasis)的病原体[1]. 弓首蛔虫病是一种人兽共患寄生虫病,人和其他哺乳动物主要通过意外摄入含有T. canis感染性幼虫或虫卵的食物而感染[2]. 作为非特异性宿主,人感染后感染性虫卵可以在小肠内发育成为L2幼虫,但不能发育为成虫,L2幼虫穿过宿主小肠壁黏膜,通过循环系统移行进入机体肺脏、肝脏、肌肉和大脑等各种器官、组织中,造成器官和组织的损伤,引发宿主的免疫和炎症反应[3-4],从而出现不同的临床症状,如隐性弓首蛔虫病(covert toxocariasis,CT)、神经弓首蛔虫病(neurological toxocariasis,NT)、内脏幼虫移行症(visceral larva migrans,VLM)及眼睛幼虫移行症(ocular larve migrans,OLM) 等[5-6],严重危害人类的身体健康.
磷脂酰乙醇胺结合蛋白(phosphatidylethanolamine binding protein,PEBP)是一个高度保守的多功能碱性胞质蛋白,其表面具有一个狭窄的空腔,是重要的配体结合位点,可结合膜磷脂、核苷酸、三磷酸腺苷等多种物质,参与维持细胞稳态,调节细胞分化、迁移和黏附等多种生物学功能[7-9]. 在寄生虫中,磷脂酰乙醇胺结合蛋白(PEBP)可参与细胞的生长、发育、繁殖和信号传导等. 如寄生恶性疟原虫PEBP能促进虫体的生长、发育和繁殖等[10-11];肝片吸虫磷脂酰乙醇胺结合蛋白通过与CD14受体进行结合来抑制p38蛋白、细胞外调节蛋白激酶(ERK)和应激活化蛋白激酶(JNK)的磷酸化,从而抑制LPS诱导的炎性反应,具有免疫调节特性[12]. 犬弓首蛔虫磷脂酰乙醇胺结合蛋白(Tc-PEPB)的研究未见报道,本研究通过克隆、鉴定Tc-pebp全长基因,采用qRT-PCR技术对犬弓首蛔虫各组织进行转录差异水平分析,以期为探讨Tc-PEBP蛋白的功能奠定基础.
全文HTML
-
犬弓首蛔虫虫体样本采自西南大学动物医学院动物医院某患病犬. 虫体用37 ℃灭菌的生理盐水洗涤去除杂质后,经形态学鉴定,将成熟的T. canis雌虫卵巢进行解剖,收集虫卵,在37 ℃培养箱中培养3~4周后,虫卵发育为L2期幼虫[13].
-
DH5α、EasyPure©胶回收试剂盒购自TransGen Biotech(全式金)公司;T-Vector pMD19(simple)、PrimeScriptTM反转录试剂盒、Taq DNA聚合酶均购自TaKaRa公司;Trizol试剂购自Invitrogen(赛默飞)公司.
-
通过形态学和分子生物学的方法对雌、雄虫进行鉴定,解剖和分离雌、雄虫的肠道,肌肉,体壁,生殖道等各个组织. 取出液氮提前预冷研钵,分别加入雌、雄虫体各组织和L2幼虫,在液氮中充分研磨成粉末. 取研磨好的粉末放入无RNA酶离心管中,使用传统的Trizol法分别提取犬弓首蛔虫成虫、L2期幼虫及各组织的RNA;采用Eppendorf核酸蛋白测定仪检测得到总RNA的浓度和纯度. 以提取的T. canis及各组织的总RNA为模板,按照PrimeScriptTM RT reagent Kit反转录试剂盒说明书来反转录合成cDNA,-20 ℃保存.
-
(1) 引物的设计与合成
根据Tc-PEBP全长基因序列(GenBank No:AAC46843.1),用Primer Premier 6.0和Primer-BLAST软件设计基因特异性引物并克隆其完整编码序列. 引物序列信息为F:5'-TTAGGCCTGCGATCGATAGAA-3';5'-AAGATAGCTAGCGTCCGGATT-3'. 引物序列送擎科兴业生物技术有限公司(重庆)进行合成.
(2) Tc-pebp基因的PCR扩增
以反转录合成的T. canis成虫及L2期幼虫的cDNA为模板,进行PCR扩增. 扩增体系为50 μL:上、下游引物(10 μM)各1 μL;Mg2+(25 mM)5 μL;10×PCR buffer(不含Mg2+)4.0 μL;dNTPs(2.5 mM)4 μL;模板(cDNA)2 μL;r×Taq酶(5 U/ μL)1 μL;dd H2O 32.0 μL[14].
PCR反应条件为:94 ℃ 3 min,94 ℃ 40 s,58 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 1 min,共35个循环;72 ℃延伸5 min,扩增产物置于4 ℃保存.
(3) 克隆及测序
PCR扩增产物经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测后,按照EasyPure©胶回收试剂盒说明书对目的PCR产物进行回收. 将回收得到的目的基因片段与pMD19-T(simple)载体进行连接,并转化至DH5α感受态细胞中. 在37 ℃ 220 r/min的条件下震荡培养60~90 min,培养结束后使用“L”型涂菌棒涂布于LB/Amp+固体培养基上(含有X-Gal和IPTG),在37 ℃恒温培养箱静置30 min后倒置,过夜培养12~16 h. 培养结束后,在平板上用接种环挑取单个白色菌落于含有900 μL LB/Amp+液体培养基的EP管中,在37 ℃ 220 r/min的摇床中过夜培养14~16 h.
(4) 序列分析
重组菌液经PCR鉴定为阳性菌液的,将其送至擎科兴业生物技术有限公司(重庆)进行测序. 将测序结果通过生物大分子序列比对搜索工具(BLAST)进行同源性比对;登录美国国家生物技术信息中心(NCBI)网站查找Tc-PEBP蛋白序列,并使用MAFFT,Clustal Omega和MUSCLE等软件对Tc-pebp基因进行多重序列比较,通过使用MEGA 7.0软件中的邻接法(Neighbour-joining,NJ法)来对Tc-PEBP蛋白序列进行系统发育进化树的构建,用Bootstrap对进化树的可靠性进行分析,共1 000个重复;并使用蛋白数据库SMART、PORTER和I-TASSER等软件预测Tc-PEBP蛋白的二级结构和功能结构域.
-
根据T. canis基因组数据(GenBank:AAC46843.1),用Primer Premier (Version 6.0) 软件设计特异性引物并克隆其完整编码序列,引物序列信息为F:5'-CGCATGTCAGTTGTACACAAA-3',R:5'-GGTTAGGCCTGCGATCGATAGAA-3'. 以18S 1:5'-AAAGGGCAGGGACGTAGTCAA-3';18S 2:5'-AATTGTTGGTCTTCAACGAGGA-3' 作为内参基因[15]. 引物序列由擎科兴业生物技术有限公司(重庆)合成.
以雌、雄虫的肌肉、体壁、肠道及生殖道等各组织的cDNA为模板,分别用Tc-PEBP和18S rRNA引物进行实时荧光定量PCR. 反应体系为50 μL:包括25 μL的SYBR Premix Ex Taq I;4 μL的cDNA;上、下游引物各2.0 μL;17 μL的ddH2O. PCR反应程序为:95 ℃预变性30 s,95 ℃变性5 s,60 ℃退火32 s,共40个循环,循环结束后收集数据进行分析.
1.1. 试验材料
1.1.1. 犬弓首蛔虫样本
1.1.2. 主要试剂
1.2. 试验方法
1.2.1. 总RNA的提取与反转录
1.2.2. Tc-pebp基因的克隆及分析
1.2.3. Tc-pebp基因的组织表达分析
-
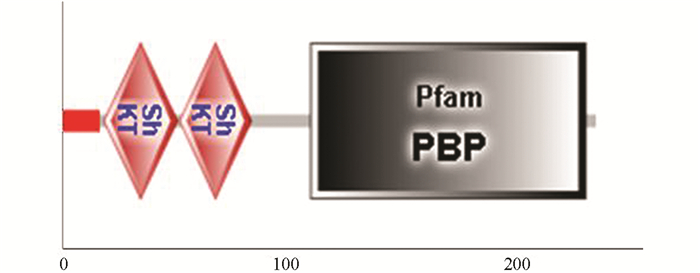
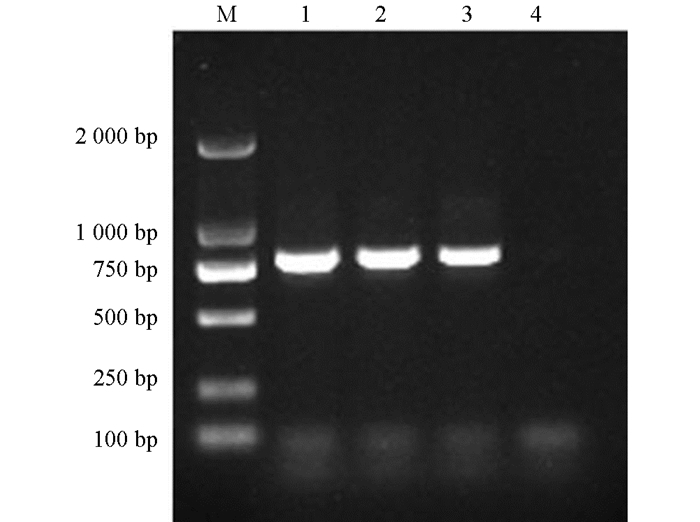
PCR扩增产物经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,Tc-pebp在约800 bp处可见相应条带,与理论大小相符;阴性对照没有条带出现(图 1). 将测序获得的碱基序列进行分析,结果显示Tc-pebp基因的完整编码区序列为789 bp,该序列含有一个完整编码区,共编码262个氨基酸,预测蛋白相对分子质量为2.6×104,功能结构域分析结果显示1~20个氨基酸为信号肽,第22~58位、第59~94位为2个重复的ShKT结构域,第123~257位有PBP保守结构域(图 2).
-
通过WormBase ParaSite[16]和GenBank检索,将Tc-PEBP蛋白氨基酸序列与4个线虫的PEBP蛋白氨基酸序列进行多重序列比对. 这些序列分别是猪蛔虫Ascaris suum(GenBank No. AEUI03000057.1)、贝拉中杆线虫Mesorhabditis belari(GenBank No. UZWA01000301.1)、秀丽隐杆线虫Caenorhabditis elegans(GenBank No. NP_001300105.1)、异尖线虫Anisakis simplex(GenBank No. UYRR01001265.1),结果发现均具有PBP保守结构域(图 3).
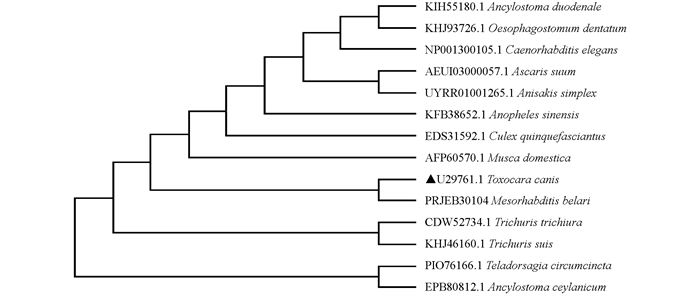
将Tc-pebp编码的氨基酸序列与通过WormBase ParaSite[16]和GenBank收录的十二指肠钩虫Ancylostoma duodenale(GenBank No. KIH55180.1)、猪蛔虫A. suum(GenBank No. AEUI03000057.1)、秀丽隐杆线虫C. elegans(GenBank No. NP_001300105.1)、有齿食道口线虫Oesophagostomum dentatum(GenBank No. KHJ93726.1)、贝拉中杆线虫M. belari(GenBank No. UZWA01000301.1)、异尖线虫A. simplex(GenBank No. UYRR01001265.1)、中华按蚊Anopheles sinensis(GenBank No. KFB38652.1)、家蝇Musca domestica(GenBank No. AFP60570.1)、环纹背带线虫Teladorsagia circumcincta(GenBank No. PIO76166.1)、致倦库蚊Culex quinquefasciatus(GenBank No. EDS31592.1)、锡兰钩虫Ancylostoma ceylanicum(GenBank No. EPB80812.1)、毛首鞭形线虫Trichuris trichiura(GenBank No. CDW52734.1)和猪鞭虫Trichuris suis(GenBank No. KHJ46160.1)进行多重序列比对并构建进化树,结果发现Tc-PEBP与贝拉中杆线虫M.belari(GenBank No. PRJEB30104)形成一个单独的分支,其进化关系较近(图 4).
-
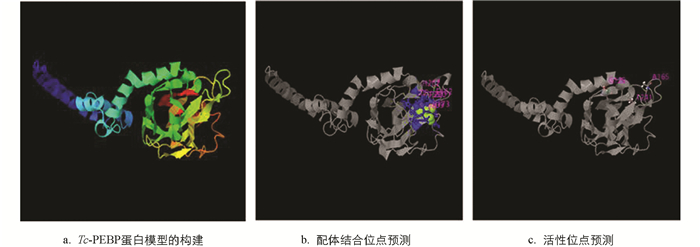
利用I-TASSER构建Tc-PEBP蛋白的三维空间,其TM最高值为0.69±0.12,标准差为6.3±3.8Å(图 5a). 根据I-TASSER显示的空间结构及功能注释,发现Tc-PEBP蛋白的结合位点为D159,F162,R173,H175,S198,T199,P200,H207和Y209(图 5b). 酶活性位点为G129,A165和T241(图 5c). 基因本体论注释表明Tc-PEBP蛋白的分子功能为结合磷脂酰乙醇胺(GO:0008429),生物学过程为调控有丝分裂(GO:0045840)和蛋白磷酸化(GO:0001933),细胞组分为粗面内质网的必要组分(GO:0005791).
-
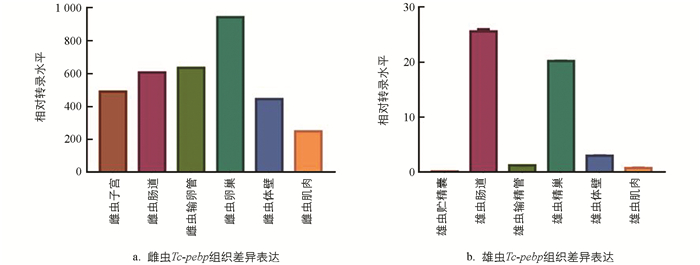
使用18S rRNA引物作为内参基因,对T. canis雌、雄虫的肌肉、体壁、肠道及生殖道等各个组织中Tc-pebp基因的转录水平进行分析,结果发现在雌虫的卵巢、输卵管、子宫、体壁、肠道和肌肉中均检测到Tc-pebp基因的表达,其中卵巢的转录水平最高,其次是输卵管,肌肉最低(图 6a);雄虫的Tc-pebp基因在肠道中表达量最高,在贮精囊中转录水平较低(图 6b).
2.1. Tc-pebp基因的克隆及鉴定
2.2. 多重序列比对及种系发育分析
2.3. 结构及功能预测
2.4. Tc-pebp的组织差异表达
-
磷脂酰乙醇结合蛋白(PEBP)在许多生理和病理过程中有着重要的作用. 如在哺乳动物体内,PEBP作为一种内源性Raf-1激酶抑制蛋白,可通过抑制细胞外调节蛋白激酶(ERK)通路的激活并与核转录因子-κB(NF-κB)上游信号分子进行结合,从而参与细胞的增殖、迁移、分化和机体的免疫防御反应等[17-19]. 在植物体内,PEBP蛋白能够长距离运输,在顶端分生组织中诱导植物的开花并调控植物的生长发育[20-22]. 在昆虫体内,PEBP可抵御外界微生物的入侵,被证明与昆虫的先天免疫防御有关[23].
本研究发现,Tc-PEBP具有ShKT结构域(ShKT domain)和PBP结构域(PBP domain)(图 3). ShKT结构域由6个保守的半胱氨基酸(SXC)组成,能够促进其他分泌蛋白如黏蛋白的形成和聚合,参与寄生虫的免疫逃避[24]. 多重序列比对显示,Tc-PEBP与猪蛔虫A. suum、秀丽隐杆线虫C.elegans、贝拉中杆线虫M.belari、异尖线虫A.simplex等均具有保守的PBP结构域,但N,C末端的保守性较差,这可能与不同物种与小分子物质结合有关[25]. PEBP可通过与膜结合对脂质进行转运[26],而T. canis中PEBP的结构和功能预测显示Tc-PEBP在脂质运输中具有一定的作用,这为今后Tc-PEBP的功能研究奠定了基础.
磷脂酰乙醇胺结合蛋白在寄生虫的生长、繁殖和胚胎发育过程中发挥着重要作用. 在秀丽隐杆线虫中PEBP存在于虫体的肌肉、体壁、阴道等部位,推测其参与早期虫体的生长发育及外阴形态的发生[27]. 在曼氏血吸虫中,磷脂酰乙醇胺结合蛋白分布于雌虫子宫、卵巢、输卵管等部位,表明其与虫体的发育繁殖有关[28];在猪蛔虫体内,磷脂酰乙醇胺结合蛋白存在于雌虫的子宫、卵巢等生殖组织中,参与维持胚胎的稳态发育[29-31]. 在本试验中,qRT-PCR结果显示雌虫体内Tc-pebp在卵巢中高量表达,说明Tc-pebp参与了T. canis雌虫的繁殖过程. 此外,在T. canis雌、雄虫肠道中均检测到Tc-pebp的表达. Gobert等[32]在日本血吸虫体内发现磷脂酰乙醇胺结合蛋白也存在于成虫肠道中,主要起摄取、运输宿主体内脂质的作用,而Tc-pebp是否参与对虫体脂质的摄取、运输过程,有待后续进一步研究.



 下载:
下载: