-
柑橘是我国栽培面积最大的果树作物,柑橘产业也是南方地区重要的农村经济支柱产业.全国柑橘产业标准化程度不高,导致果实品质优良混杂,采后果实精细分级少,影响柑橘品牌价值和产业经济效益,而进行柑橘果实分级对提高其商品价值和加工附加值具有积极作用[1].目前,我国柑橘产地主要按果实的大小、健康与病果等外表进行果实分级,而分级指标涉及内在品质较少,产地非损伤品质检测和监测技术发展缓慢. W·默科特果实肉质细嫩化渣且多汁,口感酸甜适口且风味浓,是我国南方地区主栽优良晚熟柑橘之一,对当地农业经济发展具有重要意义.
光谱技术具有无损、快速、样品无需前处理等许多独特的优点,利用光谱技术对果实品质进行检测的研究基本已涉及大部分水果[2-6]和果实中可溶性固形物(total soluble solids,TSS)、酸度(titratable acid,TA)、维生素C(vitamin C,Vc)、花青素等品质指标,研究内容主要集中于光谱获取方式、特征波段的选择、建模方法和模型评价等,但采用光谱技术目前对水果品质的检测多为一种模型只能检测一种指标,且模型的通用性较差.因此,开发利用光谱技术以实现果实多指标同时检测、通用性强、精度高的柑橘果实品质检测技术具有重要意义.
本研究以W·默科特果实为对象,分析测定果实中可溶性固形物、可滴定酸和维生素C含量,结合近红外光谱技术,采用间隔偏最小二乘法(interval partial least squares,iPLS)、间隔偏最小二乘法结合连续投影算法(Successive projections algorithm,SPA)和竞争性自适应重加权算法(Competitive adaptive reweighed sampling,CARS)提取特征波长,并采用最小二乘支持向量机回归法(Least square support vector regression,LS-SVR)和偏最小二乘回归法(Partial least squares regression,PLSR)建立果实中3种内在品质指标含量预测模型,以期为柑橘果实内在品质快速无损检测和水果智能分级技术提供参考.
全文HTML
-
供试果实采自重庆市江津区重庆市农业科学院果树研究所现代农业示范基地,品种为8年生W·默科特(W·murcott,Citrus reticulate Blanco×Citrus sinensis Osb.cv Murcott),枳橙砧(Citrus siinensis (L.) Osb. × Poncirus trifoliata (L.) Raf.).于2016-2018年度的1月中旬连续3年对选取的15株W·默科特植株进行果实采样,从树冠四周中采集健康和大小一致的果实,共获得样本180个.采用Kennard-Stone法按照3:1的比例将样本分为校正集和预测集,其中校正集135个,预测集45个.
-
将果实清洗晾干后,利用聚光科技(杭州)股份有限公司生产的便携式近红外光谱仪(波长范围1 000~2 500 nm,光谱采样间隔为1 nm,扫描次数为10次,光源采用12V,45W卤钨灯),在果面赤道线3个方向(夹角120°)各进行1次光谱扫描,每个果实共计3次,取其平均光谱为该果实光谱信息.光谱采集前用标准白板进行参比扫描.
-
对每个果实采集光谱信息以后进行单果品质检测.果实品质理化指标参照GB/T8210-2011《柑橘鲜果检验法》中方法测定,可溶性固形物用手持糖度折光仪(Pocket Pal-1,Atago,Japan)测定,可滴定酸采用酸碱滴定法测定,维生素C采用2,6-二氯靛酚滴定法测定,所有数据均进行3次技术重复.
-
利用多元散射校正(Multiplicative scatter correction,MSC)法对原始光谱数据进行预处理,以消除表面散射以及光程变化对近红外漫反射光谱的影响.
分别采用iPLS,iPLS-SPA和CARS 3种常用特征提取法对全波段光谱信息进行特征波段提取. iPLS是一种基于移动窗口法和最小二乘法的光谱特征提取方法. SPA是一种前向变量选择方法,能有效寻找含有最低限度的冗余信息变量组,使变量之间的共线性达到最小,但是SPA在寻找最低限度冗余信息变量时会增加信号的信噪比,对全波段寻找会增加计算量.因此,本文利用SPA对iPLS得到的特征波段区间进行特征波长提取. CARS是一种基于蒙特卡罗采样和PLS回归系数的特征波长选择方法,也是常用光谱特征波长提取方法之一.
采用LS-SVR和PLSR分别对不同特征筛选方法所提取的特征光谱信息构建果实TSS,TA和VC含量预测模型,同时采用K折交叉验证(K-fold Cross Validation)和网格搜索法对LS-SVR算法中核函数参数进行优化.
1.1. 实验材料
1.2. 光谱数据采集
1.3. 内在品质检测
1.4. 数据处理
-
从校正集和验证集样品果实TSS,TA和VC含量统计结果(表 1)可以看出,在所划分的校正集样品中,果实TSS,TA和VC含量最大值皆大于预测集的值,而校正集中果实TSS,TA,VC含量最小值皆小于预测集的值.说明校正集样本所覆盖的范围皆大于预测集所覆盖的范围,采用Kennard-Stone法所划分的校正集代表性较强,样本划分合理,可用于建立预测模型.
-
从果实原始近红外光谱(图 1)可以看出,在1 000~2 500 nm近红外光谱区有3个较强的吸收峰. 1 200 nm和1 920 nm左右的吸收峰,主要是O—H键各级倍频的变化,是由水分含量引起; 1 450 nm处吸收峰附近主要是C—H,—CH2键的变化,是由大分子糖类物质所引起.说明利用近红外光谱检测柑橘果实内在品质具有可行性.
-
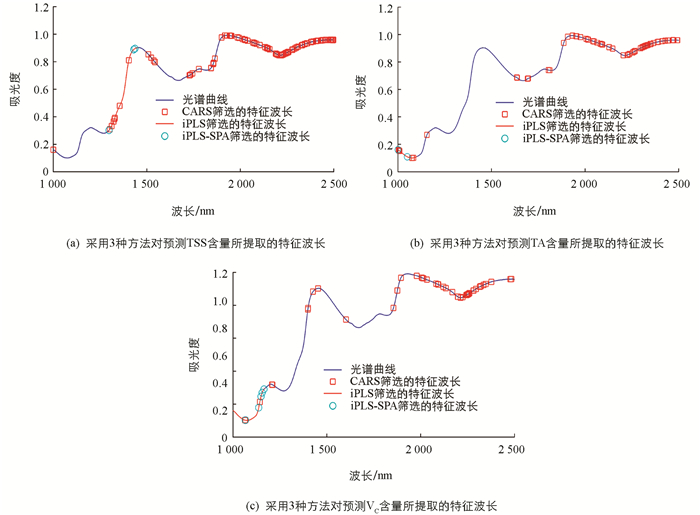
对预处理后全波段光谱分别采用CARS,iPLS和iPLS-SPA提取得到特征波长(表 2,图 2).
从表 2可以看出,采用iPLS和iPLS-SPA对TSS含量预测所筛选特征波长在1 300~1 449 nm区域,采用CARS对TSS含量预测所筛选特征波长主要为1 303~1 544 nm,1 728~1 993 nm和2 012~2 498 nm,3种方法提取的特征波长在1 300~1 449 nm区域具有交叉重叠; 对TA含量预测采用iPLS和iPLS-SPA筛选的特征波长在1 000~1 099 nm区域,采用CARS筛选的特征波长区域主要集中在1 003~1 009 nm,1 075~1 083 nm,1 907~2 494 nm,3种方法提取的特征波长在1 003~1 009 nm和1 075~1 083 nm区域具有交叉重叠; 对VC含量预测采用iPLS和iPLS-SPA筛选的特征波长在1 000~1 166 nm区域,采用CARS筛选的特征波长区域主要集中在1 064~1 066 nm,1 208~1 602 nm,1 855~2 483 nm,3种方法提取的特征波长在1 064~1 066 nm区域具有交叉重叠.
从图 2可以看出,采用不同特征提取方法所获得的特征波长区域存在差异; 3种特征波长方法皆减少了预测模型输入的数据量,其中采用iPLS-SPA所获得的特征波长个数最少; CARS提取的波长区域范围最大,但采用iPLS所提取的波长数最多.
-
将全波长1 500个变量以及CARS,iPLS和iPLS-SPA提取的特征波长对应光谱信息作为输入,建立TSS,TA和VC含量LS-SVR和PLSR预测模型(表 3).采用校正集和预测集均方根误差(RMSEC,RMSEP)和相关系数(RC,RP)作为模型的评价指标.从表 3可以看出,采用全波段,iPLS和iPLS-SPA提取的特征波长对应光谱信息作为模型输入,建立的果实TSS含量LS-SVR和PLSR预测模型的预测集和建模集的相关系数和RMSE接近,但采用CARS结合LS-SVR获得的模型精度最高,预测相关系数达到0.91,且RMSEP值最低; 采用全波段,iPLS和iPLS-SPA结合PLSR建立的模型对果实TA含量预测精度高于LS-SVR模型,采用CARS筛选波长对应光谱信息建立的PLSR和LS-SVR模型比采用其他3种波长对应光谱信息建立的模型预测精度都高,且采用CARS结合LS-SVR建立模型对TA含量预测相关系数达到0.85,且RMSEP值最低; 采用全波段,iPLS和iPLS-SPA结合LS-SVR和PLSR建立的VC含量模型稳定性和精度皆较低,而采用CARS提取的特征波长对应光谱信息建立的LS-SVR预测模型对VC含量预测精度最高,预测相关系数达到0.91,且RMSEP值较低.根据预测模型不但要有高的相关系数,较小的RMSEP和RMSEC,且RMSEP,RMSEC之间的差异要较小的模型性能评判原则,得出采用CARS提取的特征波长建立的LS-SVR模型对W·默科特果实TSS,TA和VC含量预测效果最为理想.
2.1. 果实TSS,TA和VC含量
2.2. 果实光谱反射值曲线
2.3. 特征波长提取
2.4. 模型的建立
-
利用光谱技术对果实品质进行检测已有较多研究,研究者采用较多的波长范围主要集中在可见光和近红外区域.本研究采用1 000~2 500 nm近红外波长区域,从W·默科特果实光谱反射曲线来看,在该区域该波形与其他柑橘品种基本一致[7-9],与甜柿[10]、西瓜[11]、黄桃[12]等果实也具有相同的吸收峰和波形.在1 000~1 450 nm波段区域,该波段区域与柑橘果汁[7-8]光谱曲线具有相同波形和吸收峰,说明1 000~1 450 nm波段对光谱技术检测果实内部品质紧密相关.
特征提取是光谱数据挖掘中的一个核心环节,进行特征波段筛选可以缩减建模输入参数,减少模型运算时间、消除多余干扰信息,提高模型的预测精度.本研究采用iPLS,iPLS-SPA和CARS 3种方法进行特征波长提取,获得的特征波长区域存在差异,说明建模采用的特征波长与采用的提取方法相关.本研究果实TSS含量最佳模型采用的特征光谱波段与Guo等[13]建立的桃,田喜等[7]建立的脐橙,Cunha Junior等[14]建立的棕榈果TSS预测最佳模型采用的特征波长相互交叉重叠,所采用的特征波长集中于1 303~1 544 nm,1 728~1 993 nm和2 300~2 399 nm区域.果实TA含量最佳模型采用特征光谱波段与代芬等[15]建立的砂糖橘,Guo等[16]建立的枣和Louw等[17]建立的李果实的TA含量预测最佳模型采用的特征波长相互交叉重叠,所采用的特征波长主要集中于1 900~2 300 nm区域.果实VC含量最佳模型采用特征光谱波段与夏俊芳等[18]建立的脐橙以及高升等[19]、陈辰等[20]建立的红提果实VC含量预测最佳模型采用的特征波长相互交叉重叠,所采用的特征波长集中于1 064~1 066 nm,1 208~1 602 nm和1 855~2 483 nm区域.由于采用设备仪器、波长筛选方法以及涉及水果种类差异等,研究者采用光谱技术对水果品质指标检测所采用的波长不一致,即使是针对相同品种的水果不同研究者建模采用的波长范围也不一致.本研究最终采用CARS结合LS-SVR建立了W·默科特果实SSC,TA和VC含量预测的通用模型,但果实内在品质包括较多指标,是一个较为复杂的系统[21-22],该模型对其他柑橘品种果实中SSC,TA和VC含量的预测精度及适用性仍需进行验证.建立采用波数个数少、预测精度高、通用性强的果实内部品质含量模型仍是目前研究的重点.
本研究采用两种方法建立了柑橘果实内在品质预测模型,PLSR是化学计量学分析过程中最常用的多元线性建模方法,PLSR在计算理化指标与光谱信息之间关系是依靠寻找线性相关性来实现的; LS-SVR是一种基于统计学习理论的机器学习算法,在计算过程中采用非线性映射的核函数,可用于处理非线性回归问题.总体上,采用相同的数据建立的LS-SVR模型预测精度高于PLSR模型,该结果与詹白勺等[23]建立的对香梨可溶性、牛晓颖等[24]建立的对草莓固酸比和可滴定酸及黄康等[25]建立的对番茄汁糖酸度预测模型结果一致.模型预测结果说明,果实内在品质理化指标与光谱信息的变化关系为非线性关系,宜采用非线性算法构建果实内在品质理化指标预测模型.
-
本文利用近红外光谱技术对W·默科特果实的SSC,TA和VC含量进行了定量分析研究,得出采用CARS,iPLS和iPLS-SPA 3种方法可极大地简化模型; LS-SVR与PLSR相比更适用于果实内在品质定量分析模型的建立; 利用近红外光谱技术,采用CARS筛选特征波长结合LS-SVR可用于W·默科特果实的SSC,TA和VC含量的同时检测.




 下载:
下载: