-
文中所研究的图均为有限无向图且均是简单图.设G=(V,E)表示顶点集为V,边集为E的简单图.用Δ和δ分别表示图G的最大度和最小度,ni表示图中度为i的点的个数,P表示路.
六角系统(HS)是指平面上若干个全等的正六边形所组成的网络,其中每个六边形的边都分别平行于3个固定的方向,且它们覆盖的平面区域(称为HS的区域)是连通的.六角系统是苯系化合物分子结构的数学模型,这模型的数学结构与分子的化学特性有着密切的关系,因此对六角系统的研究对于化学理论有着重要的意义.文献[1]研究了关于六角系统的Wiener指标.文献[2]针对渺位六角系统的Wiener指标,降低了边的Wiener指标.文献[3-4]分别对六角系统的顶点度极值进行了研究.
然而对于六角系统的点可区别边染色的研究并不多见.文献[5]给出了点可区别边染色的定义.文献[6]提出了一个著名的猜想:对任意一个点可区别边染色图G,它的点可区别边色数为π(G)或π(G)+1,其中π(G)为图G的边组合度且满足
对于此猜想目前仍没有得到解决,但是对于一些特殊图是成立的,例如完全图、完全二部图、路、圈以及一些树[6]等.近年来,学者们一直致力于研究各类图的点可区别边色数,并得到了一些结果.文献[7]证明了:对于阶数n≥3的连通图,若σ2(G)≥2n/3,则它的点可区别边色数不超过Δ+5,其中σ2(G)表示G中两个不相邻的点的最小度和.文献[8]证明了:若树T满足n2(T)≤n1(T),且树的直径为3或任意两树之一的直径为4时,它的点可区别边色数为n1(T)+1,否则它的点可区别边色数为n1(T).
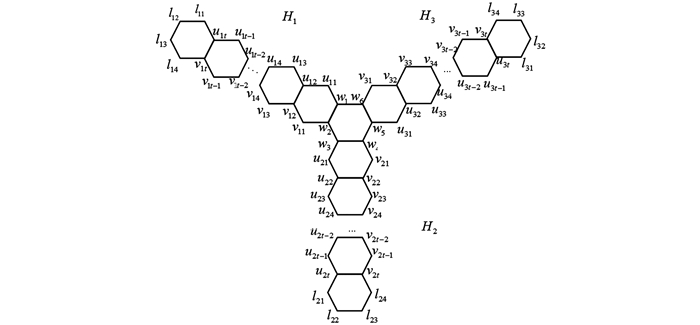
由于六角系统独特的图结构,研究它的点可区别边染色还是有一定难度的.本文研究了一类特殊的六角系统,它是3个由分别为p个直线排列的正六边形组成的直链与一个正六边形组成的中心对称图,简称p(p≥1)阶T-型六角系统链,记作H.本文首先用π(H)+1种颜色用染色算法对H(p≥4)中所有2度点所关联的边进行着色,又通过分析3度点的色集合,对个别边进行调色之后,可以满足H的点可区别边着色的.当p≤3时,用π(H)种颜色对H的边进行着色,并给出具体的染色方法,从而证明H的点可区别边着色也满足文献[6]中的猜想.
定义1[6] 对图G,设映射f:E(G)→{1,2,…,k}满足对∀uv,uw∈E(G),有f(uv)≠f(uw),则称f为G的k-正常边染色,记为k-PEC.若图G(V,E)不含孤立边,且最多有一个孤立点,且满足对∀u,v∈V(G),如果u≠v,有C(u)≠C(v)成立,则称f为G的k-点可区别边染色,记为k-VDEC.记χvd′(G)=min{k:G有k-VDEC}是图G的点可区别边色数,其中C(u)={f(uv):uv∈E(G)}.特别地,若对任意u,v满足d(u)=d(v)=i,均有C(u)≠C(v),则称f为关于G的i度点的点可区别边染色.显然对于任意图G(V,E)的点可区别边染色,均有χvd′(G)≥π(G)成立.
HTML
-
p(p≥1)阶T-型六角系统H是由2度点和3度点组成的,其中n2=6p+6,n3=6p.它的边组合度为
由于当θ≥5时,
$\left( \begin{array}{l} \theta \\ 3 \end{array} \right) \ge \left( \begin{array}{l} \theta \\ 2 \end{array} \right) $ ,而对p≥1,都有θ≥5成立,因此此时
$ \pi \left( H \right) = k \cdot \left\lceil {\frac{{1 + \sqrt {48p + 49} }}{2}} \right\rceil . $ 接下来将给出一个染色的算法,对p(p≥4)阶T-型六角系统H的所有2度点相关联的边进行着色,直到没有边剩余.
首先把
$ \left( \begin{array}{l} k\\ 2 \end{array} \right) $ 种2色集合按顺序排列出来,如图 1.根据图 1中色集合的排列,得到如下染色序列,并记c(i)为上述序列中第i个位置所对应的颜色:
1,2,1,3,1,4,1,5,1,6,1,7,1,8,…,1,k-1,1,k;
2,3,2,4,2,5,2,6,2,7,2,8,…2,k-1,2,k;
3,4,3,5,3,6,3,7,3,8,…,3,k-1,3,k;
4,5,4,6,4,7,4,8,…,4,k-1,4,k;
…
k-1,k.
其次,将H的各个分支按逆时针方向标记为H1,H2,H3,将中心六边形的各顶点按逆时针方向依次标记为w1,w2,w3,w4,w5,w6,再分别对各分支的顶点进行标号,如图 2,其中t=2p-2.
-
算法1
输入:p(p≥10)阶T-型六角系统H.
输出:关于H的所有2度点可区别k+1边着色.
步骤1 把u2tl21l22l23l24v2t依次赋予颜色2,3,4,5,1;把u3tl31l32l33l34v3t依次赋予颜色1,4,2,5,3.
步骤2 去掉图 1中前4列的10个2色集合{1,2},{1,3},{1,4},{1,5},{2,3},{2,4},{2,5},{3,4},{3,5},{4,5}之后,再重新排序,得到新序列如下:
1,6,1,7,1,8,…,1,k-1,1,k;
2,6,2,7,2,8,…2,k-1,2,k;
3,6,3,7,3,8,…,3,k-1,3,k;
4,6,4,7,4,8,…,4,k-1,4,k;
…
5,6,5,7,5,8,…,5,k-1,5,k;
6,7,6,8,6,k-1,6,k;
7,8,7,k-1,7,k,…,k-1,k.
容易看出对任意i均满足c(i)≠c(i+1).当i是偶数时,c(i)≥6,c(i)>c(i-1),c(i)≠c(i+2);当i是奇数时,c(i)是递增函数.
步骤3 令i=1.
步骤 4 令P(1)=w1u11u12u13u14…u1t-1u1tl11l12,P(2)=l13l14v1tv1t-1…v14v13v12v11w2,P(3)=w3u21u22u23u24…u2t-1u2t,P(4)=v2tv2t-1…v24v23v22v21w4,P(5)=w5u31u32u33u34…u3t-1u3t,P(6)=v3tv3t-1…v34v33v32v31w6.此时对路P(1),P(2),P(3),P(4),P(5),P(6)进行边着色.记u为路P(i)(i=1,…,6)中的任意点,u′为点u的后继顶点.令u=w1,则u′=u11.把边uu′染以c(i)色,此时令u=u′,i=i+1.
步骤5 若u=l12,则说明路P(1)被染完,执行.
令u=l13,u′=l14.将边uu′染以c(i)色.此时令u=u′,i=i+1.
若u=w2,则说明路P(2)被染完,执行.
令u=w3,u′=u21.将边uu′染以c(i)色.此时令u=u′,i=i+1.
若u=u2t,则说明路P(3)被染完,执行.
令u=v2t,u′=v2t-1.将边uu′染以c(i)色.此时令u=u′,i=i+1.
若u=w4,则说明路P(4)被染完,执行.
令u=w5,u′=u31.将边uu′染以c(i)色.此时令u=u′,i=i+1.
若u=u3t,则说明路P(5)被染完,执行.
令u=v3t,u′=v3t-1.将边uu′染以c(i)色.此时令u=u′,i=i+1.
若u=w6,则说明路P(6)被染完.
结束.
步骤6 引入新色k+1,将边l12l13染以k+1色.
通过上述算法1,能够得到一个关于T-型六角系统H的所有2度点的点可区别(k+1)-边染色.将w1w2w3w4w5w6w1依次赋予颜色4,1,2,3,2,5.此时对于T-型六角系统H,只有边ui2vi2,ui4vi4,…,uit-2vit-2,uitvit(i=1,2,3)没有被染色,又因这些边互不相交,所以可以用新色k+1对其同时进行着色.
下面对3度点wi(i=1,…,6)进行分析,可设C(w1)={4,5,a},C(w2)={1,4,b},C(w3)={1,2,d},C(w4)={2,3,f},C(w5)={2,3,g},C(w6)={2,5,h}.由于染色算法的顺序性且路Pi(i=1,…,6)均为偶数阶,则b≠d,f≠g,且a=1;b,f,h≥6;d≥3;g≥4.否则,分别有:
成立,即分别有:
此时,分别有
$ k < \frac{{15 + \sqrt {57} }}{2} $ ,k<9.不符合题意.于是点wi是正常边染色且色集合均可区分.又因点wi(i=1,…,6)的色集合不含k+1色,于是点wi与其他3度点均可区分.上述染色算法对任意的uij,vij(i=1,2,3;j=2,4,6,…,t-2,t)均满足C(uij)≠C(vij),且除了点u2t,v2t,u3t,v3t外,其他点的色集合均可互相区别.
下面考虑u2t,v2t,u3t,v3t这4个三度点的色集合,对u2tv2t,u3tv3t两条边进行调色.
分别设边v3t-2v3t-1,v3t-1v3t,u3t-1u3t,v2t-2v2t-1,v2t-1v2t,u2t-1u2t上的颜色依次为:x1,x2,x3,y1,y2,y3.由于x1≠x2,x1≠x3且x1≥6,于是可以用颜色x1对u3tv3t正常染色,此时点v3t的色集合为{3,x1,x2},u3t的色集合为{1,x1,x3},又由于x2≥4,x3≥6,于是除了点u2t,v2t外均可区别.同理可以用颜色y1对u2tv2t正常染色,此时点v2t的色集合为{1,y1,y2},u2t的色集合为{2,y1,y3},其中y1,y3≥6,y2≥3.容易看出,u2t的色集合与其他点的均可区分,而点v2t的色集合有可能与点u3t或点w2的区分不开.根据染色序列的性质能够得到x1,x3>y2,于是点v2t的色集合与点u3t的一定可区别.若点v2t的色集合与点w2的相同,此时取颜色c≥6且不同于b,y2,y3即可.又由于p≥10,于是χvd′(H)≥π(H)=12,因此颜色c的取法至少有4种可以对边u2tv2t正常着色.
至此,就用算法1得到了p(p≥10)阶T-型六角系统H的(k+1)-点可区别边染色.
-
当4≤p≤9时,k=π(H),于是9≤k≤12,其算法与算法1类似,这里不再赘述,只需调整部分颜色,并将w1w2w3w4w5w6w1依次赋予颜色2,5,4,2,3,4.此时d≤3.若d≥4,则
于是求得k≤5或k≥16,矛盾.
1.1. p(p≥10)阶H的点可区别边染色
1.2. p(4≤p≤9)阶H的点可区别边染色
-
定理1 对p(p≥1)阶T-型六角系统H,均有
证 由于
求得
于是
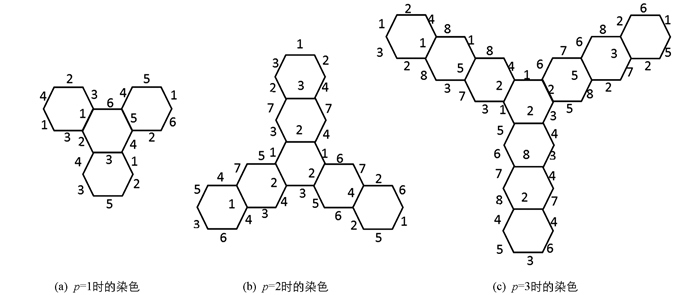
首先,分别给出p=1,2,3时的p阶六角系统H的点可区别边染色,如图 3.
p=1时,π(H)=6,χvd′(H)=6;
p=2时,π(H)=7,χvd′(H)=7;
p=3时,π(H)=8,χvd′(H)=8.
因此当p=1,2,3时,满足题意
当p≥4时,由算法1可得
至此,就得到了p(p≥1)阶T-型六角系统H的(k+1)-点可区别边染色,它的点可区别边色数满足
于是定理1得证.因此p(p≥1)阶T-型六角系统H的点可区别边染色符合文献[6]中的猜想.







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: