-
Navier-Stokes方程是描述流体运动规律的一类典型的非线性方程,其研究对人们认识和控制湍流格外重要,并被广泛应用于天气、海流等方面.近几十年来,用有限元方法数值求解Navier-Stokes方程吸引了许多研究者[1-3].而后处理的思想最初是在文献[4]中基于Fourier谱方法提出的,文献[5]将该方法应用于混合有限元方法提出了后处理的混合有限元方法.该方法主要分为两步:第一步,在粗网格上求解一个非线性系统,得到最后时刻T的有限元解uH;第二步,在最后时刻T,对第一步所得解进行后处理,主要通过在细网格上(或用高阶元)求解一个线性的Stokes问题[6],或一个线性Ossen类型的问题[7],或者一个Newton类型的问题[8].理论分析和数值实验表明:在选择合适的网格尺寸的条件下,后处理的混合有限元方法与标准的有限元方法相比收敛精度提高了一阶.由于完全非线性问题要在粗网格上求解,而对流占优的流体具有不稳定性,所以用后处理的方法模拟大雷诺数流问题具有一定的挑战性.本文中,我们把前面提到的3种后处理的有限元方法和亚格子稳定化方法[9]相结合,提出了3种稳定化的后处理混合有限元方法.
HTML
-
定义1 设Ω是
${{\mathbb{R}}^{d}}$ (d = 2,3)中具有齐次Dirichlet边界条件的有界区域,我们考虑下面的Navier-Stokes方程:其中:u:Ω→
${{\mathbb{R}}^{2}}$ 表示速度矢量,p:Ω→$\mathbb{R}$ 表示压力,f:Ω→${{\mathbb{R}}^{2}}$ 表示流体驱动的体积力,ν>0为流体粘性系数,u0是使得▽·u0 = 0的初始速度,并且ut = ∂u/∂t,定常数T表示最后时刻.下面针对定义1提出的数学问题,我们引进两个Hilbert空间:
对H,V分别赋予L2(Ω)d空间和H01(Ω)d空间的内积.用‖·‖l表示Sobolev空间Wl,q(Ω)d的范数,‖·‖-l表示其对偶空间的范数.后面还会涉及到商空间Hl(Ω)/
$\mathbb{R}$ ,其范数定义为:设
$\mathscr{T}$ h = (τih,ϕih)i∈Ih(h>0)是区域Ωh的准均匀网格剖分,其中h是单元τih∈${{\mathscr{T}}_{\mathit{h}}}$ 的最大直径,ϕih:τ0→τih为单射.当r≥2时,基于网格剖分${{\mathscr{T}}_{\mathit{h}}}$ ,我们定义下列有限元空间:其中Pr-1(τ0)表示定义在τ0上的至多r-1次多项式空间.
接下来,我们考虑Hood-Taylor元(Xh,r,Qh,r-1),其中
并且这个有限元对(Xh,r,Qh,r-1)满足inf-sup条件[6].
根据非线性项b(·,·,·)的定义[9],我们具体给出离散的非线性项bh(·,·,·)为:
亚格子模型是基于一个椭圆型投影算子
${{\mathit{\Pi }}_{h}}:{{H}_{0}}^{1}{{\left(\mathit{\Omega } \right)}^{d}}\to {{R}_{1}} = \left\{ v\in {{H}_{0}}^{1}{{\left(\mathit{\Omega } \right)}^{d}}:v\left| _{\pi _{i}^{h}} \right.\in {{({{p}_{1}})}^{d}}, \forall {{\tau }_{i}}{{~}^{h}}\in {{T}_{h}} \right\}$ 所定义,其中算子Πh的定义为:下面根据投影算子Πh,定义亚格子稳定项为:
其中α>0是稳定化参数,通常α = o(hs)(s是与所使用有限元空间的阶数有关的参数).
下面在T时刻逼近问题(1)-(4).基于3种后处理的有限元方法[6-8]和亚格子稳定化方法[9],我们的亚格子稳定化的后处理有限元方法具体如下:
算法1 基于Stokes问题的稳定化后处理有限元方法.
1) 给定u0h逼近u(0),寻找uh:[0,T]→Xh,r和Qh,r-1使得:
其中
${{{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\dot{u}}}}}_{h}} = \partial {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{u}}}_{h}}/\partial t$ ,并且通常取u0h = Sh(u0),Sh是离散Stokes投影[6].2) 对离散的速度和压力(uh(T),ph(T))后处理,寻找
$({{{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\tilde{u}}}}}_{{\tilde{h}}}}, \text{ }{{{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\tilde{p}}}}}_{{\tilde{h}}}})\in \left(\tilde{X}, \tilde{Q} \right)$ 使得:其中后处理的有限元
$\left(\tilde{X}, \tilde{Q} \right)$ 有以下两种取法:方法1 更细网格上的同阶Hood-Taylor元
$\left(\tilde{X}, \tilde{Q} \right) = ({{X}_{\tilde{h}, r}}, {{Q}_{\tilde{h}, \text{ }r-1}}), \ r\ge 3, \ \tilde{h} < h$ .方法2 相同网格上的高阶Hood-Taylor元
$\left(\tilde{X}, \tilde{Q} \right) = ({{X}_{\tilde{h}, r+1}}, {{Q}_{\tilde{h}, \text{ }r}}), \ r\ge 3, \ \tilde{h} = h$ .算法2 基于Newton型问题的稳定化后处理有限元方法.
1) 给定uh(0)逼近u(0),寻找uh:[0,T]→Xh,r和ph:[0,T]→Qh,r-1,使得(uh,ph)满足(5)-(6)式;
2) 对离散的速度和压力(uh(T),ph(T))后处理,寻找
$({{{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\tilde{u}}}}}_{{\tilde{h}}}}, \text{ }{{{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\tilde{p}}}}}_{{\tilde{h}}}})\in \left(\tilde{X}, \tilde{Q} \right)$ 使得:算法3 基于Ossen型问题的稳定化后处理有限元方法.
1) 给定uh(0)逼近u(0),寻找uh:[0,T]→Xh,r和ph:[0,T]→Qh,r-1,使得(uh,ph)满足(5)-(6)式;
2) 对离散的速度和压力(uh(T),ph(T))后处理,寻找
$({{{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\tilde{u}}}}}_{{\tilde{h}}}}, \text{ }{{{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\tilde{p}}}}}_{{\tilde{h}}}})\in \left(\tilde{X}, \tilde{Q} \right)$ 使得:
-
本节将利用FreeFem++软件[10]进行数值实验来证明算法的有效性和比较3种亚格子稳定化后处理混合有限元方法的不同.在实验中,Hood-Taylor元用于空间离散,算法中第一步的非线性系统由Crank-Nicolson Admas-Bashforth方法求解,第二步在相同的网格上用高阶Hood-Taylor元P3-P2元后处理.
-
特别地,对于算法1,我们选择Navier-Stokes方程的准确解为:
其中,求解区域Ω = [0, 1]×[0, 1] ⊂
${{\mathbb{R}}^{2}}$ ,并且取ν = 1,T = 0.1,α = 0.1 h2|log(h)|. 表 1给出了T时刻稳定化的混合有限元逼近解和后处理所得解的第一个分量的L2-范误差,其中‖u(T)-uNh‖0表示稳定化的混合有限元速度解的误差,${{\left\| \mathit{\boldsymbol{u}}\left(T \right)-{{{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\tilde{u}}}}}_{N}}^{h} \right\|}_{0}}$ 表示稳定化后处理速度解的误差,第二个分量类似可得;表 2为H1-范误差;表 3为压力解的误差比较,其中‖P(T)-Ph‖0为稳定化的混合有限元解的压力误差,${{\left\| \mathit{\boldsymbol{P}}\left(T \right)-{{{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\tilde{P}}}}}_{h}} \right\|}_{0}}$ 表示稳定化后处理压力误差.通过表 1-3可知,稳定化的后处理混合有限元方法确实提高了稳定化的混合有限元解的精确度.为了对比3种算法,取网格尺寸h = 1/160,时间步长Δt = 1/8 000,分别取ν = 1,0.1,0.01和0.001,进行数值求解.数值结果在表 4-6中给出,通过比较发现:从花费时间的长短来看,除ν = 1以外,在其它情况下稳定化的Newton型后处理花费的时间相对较多,而稳定化的Ossen型后处理花费的时间相对较少.从精确度来看,用3种算法所得速度的L2-范误差基本一致,但由算法2和算法3所得的速度的H1-范误差和压力的L2-范误差比算法1更准确.
-
在这个实验中,我们考虑一个定义在Ω = [0, 6]×[0, 1]上的圆柱绕流问题,其中该圆柱的圆心(x,y) = (1,0.5),半径为0.15.取入流速度为
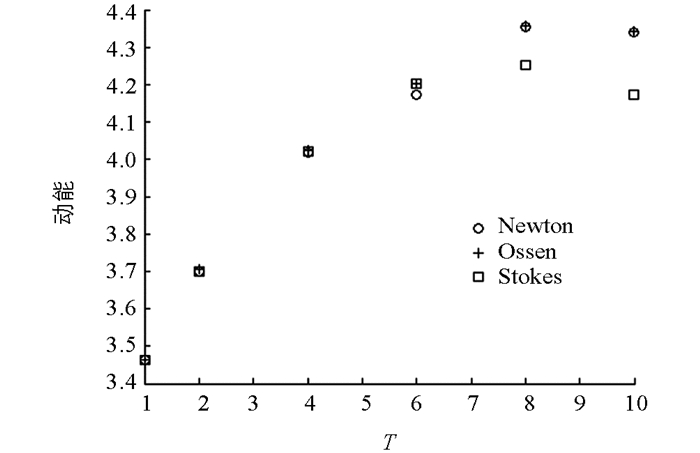
并且在其它边界上满足无滑动边界条件[11].在这个问题中,Hood-Taylor元用于空间离散,粘性系数ν = 0.001.设置网格尺寸为h = 1/12,稳定化参数α = 0.1h2|log(h)|,时间步长Δt = 0.001,分别取最后时刻T = 1,2,4,6,8,10. 图 1描述了3种算法关于动能和时间T的关系.从图中可以看出在T = 1,2,4,6时3种算法所得解的动能差距不大,但在T = 8,10时算法2和算法3所得解的动能比算法1的大.
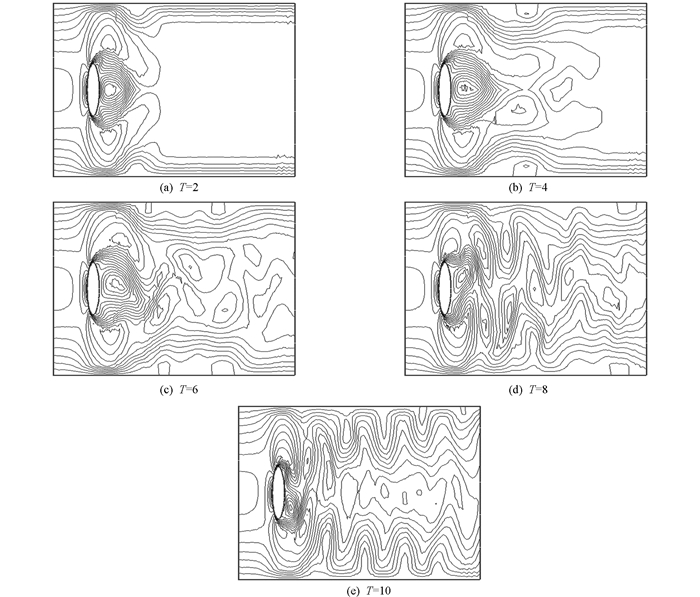
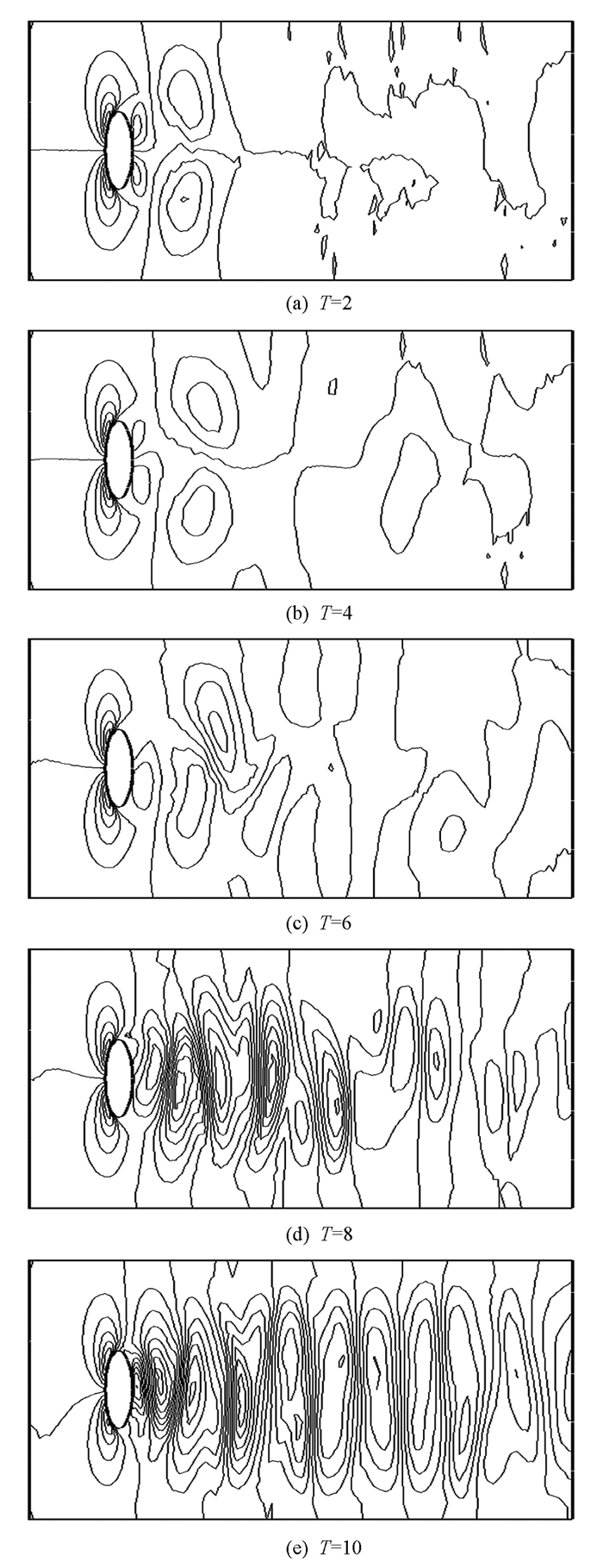
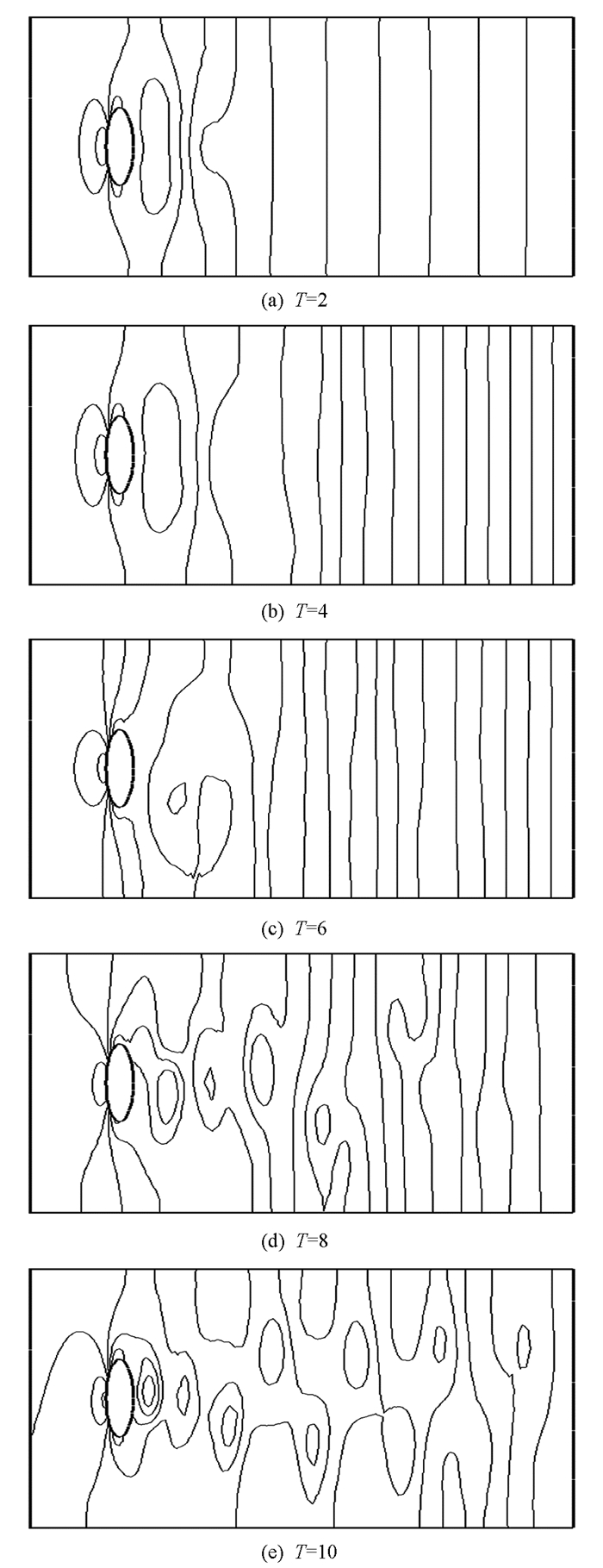
图 2描绘了在T = 1,2,4,6,8,10的情况下,算法2在圆柱周围的速度分量
${{{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\tilde{u}}}}}_{\tilde{h}1}}$ 的等值线;图 3是速度分量${{{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\tilde{u}}}}}_{\tilde{h}2}}$ 的等值线;而图 4是压力等值线.对于算法1和算法3,可得到类似的结果.
2.1. 解析解
2.2. 圆柱绕流
-
在这篇文章中,我们主要通过数值实验研究了3种基于亚格子模型的后处理混合有限元方法,实验结果表明:在选取适当的稳定化参数和网格尺寸的条件下,3种稳定化的后处理有限元方法提高了稳定化的混合有限元解的精确度,并且收敛阶也明显提高了一阶.但是从计算时间看,除ν = 1以外,在其它情况下稳定化的Newton型后处理花费的时间相对较多,而稳定化的Ossen型后处理花费的时间相对较少.从精确度来看,用3种算法所得的速度的L2-范误差基本一致,但Newton型后处理和Ossen型后处理方法所得的速度的H1-范误差和压力的L2-范误差比Stokes型后处理方法更有效.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: