-
分布式优化在数字通信领域的理论及应用引起了广大学者的关注[1-11].
受文献[3, 5]的启发,本文进一步考虑了在有向网络下的带确定型量化的分布式push-sum次梯度算法,并讨论了确定型量化对算法的收敛性影响.对于强凸分布式优化问题,在确定型通讯量化的情况下,我们提出的算法能收敛到最优解的附近,其收敛率为
$O\left( {\frac{{\ln \tau }}{\tau }} \right)$ .最后,数值实验表明量化精度越高,越接近最优.
HTML
-
考虑在一个具有n个节点的多个体网络中,每个个体仅知道其自身的目标函数,且仅与其邻居进行局部信息交换,使所有个体的目标函数之和达到最优,即如下的一个多个体网络分布式优化问题[2]:
其中每个个体i仅知道其局部目标函数fi(z):ℝd→ℝ,z是全局决策变量.
定义1 如果对任意x,y∈ℝd,有
则称函数f是ℝd的μ强凸函数,其中常数μ≥0,g(y)是f在点y的次梯度,这里‖·‖是欧几里得范数.
定义2 如果对任意x,y∈ℝd,有‖f(x)-f(y)‖≤L‖x-y‖称函数f是L-利普希茨连续.
假设1 对每一个i,i=1,…,n,函数fi是μi-强凸函数;并且它是Li-利普希茨连续的,常数μi≥0,Li≥0.记
$L = \sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {{L_i}} $ .如果假设1成立,则问题(1)存在唯一全局最优解,记为z*,即
若将网络中每个个体看作是一个节点,则多个体网络中个体间的信息通信可以表述为一个时变的有向图G(t)=(V,E(t)),其中V={1,2,…,n}为顶点的集合,E(t)⊆V×V为边的集合表示个体间的信息交流过程.分别用Niin(t)和Niout(t)表示个体i在t时刻的内邻居点和外邻居点集,即
用di(t)表示个体i在t时刻的外度,即di(t)=|Niout(t)|.假设个体i在t时刻仅知道它的外度di(t).
假设2 有向图序列{G(t)}是B强连通的,即存在正整数B,对∀k≥1使得Ek(t)∪Ek+1(t)∪…∪Ek+B-1(t)是连通的.
-
假设所有的个体仅能向与之相邻的节点传递量化过后的信息,但是所有节点能存储实值的数据.本文采用确定型量化规则[4-5]如下:假设待量化的值x∈[-M,M],M充分大;有l个采样点将区间[-M,M]均匀分为l-1个子区间,采样点集合记为m={m1,m2,…,ml},并且m1=-M,ml=M,则每个子区间的长度为
$\frac{1}{\Delta }$ ,即$\frac{1}{\Delta }$ =mi+1-mi,定义这里
$\left\lfloor x \right\rfloor $ 表示x向下取整到某个最近的采样点mi(i=1,…,l).令v=Q[x]-x表示量化误差,根据上述的量化规则,有如下关系式成立
1.1. 问题描述
1.2. 量化
-
下面将研究经过量化后的分布式push-sum次梯度算法对优化问题(1)的影响.本文提出如下带量化的分布式push-sum次梯度算法(Q-PSDSG):
第0步 初始化,对i=1,…,n,取xi(0)∈ℝd满足‖xi(0)‖有界;yi(0)=1.
第1步 对每个i=1,…,n,更新
第2步 t=t+1,转到第1步.
这里步长α(t)>0是单调递减的,gi(t)是fi在zi(t)的随机次梯度.
-
为了简便,记所有个体的状态平均值为
$\mathit{\boldsymbol{\bar x}}(t) = \frac{1}{n}\sum\limits_{j = 1}^n {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{x}}_j}} (t)$ ,个体i经过量化后的误差为vi(t)=Q[xi(t)]-xi(t).定义通讯权矩阵A(t)如下:引理1 若假设1和2成立,那么对∀y∈ℝd和t≥0,有以下不等式成立:
这里
$q = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {L_i^2} $ .证 由x(t)的定义和(6)式可得,
令y∈ℝd为任意变量,通过(7)式得:
则有
因为fi是强凸函数且是次梯度有界的,由文献[3]中引理2的证明类似可知对∀y∈ℝd有
注意到
并结合(8),(9)式可以得到
其中
$q = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{\left( {{L_i}} \right)}^2}} $ ,从而引理1得证.下面给出一个关于算法Q-PSDSG的收敛性结果.
定理1 假设1和假设2成立并假设步长α(t)单调递减且满足
$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{t \to \infty } \alpha \left( t \right) = 0$ ,则对任意的i=1,…,n和t≥0有其中
证 在引理1中,取y=z*有
接下来估计F(x(t))-F(z*).一方面,根据假设1知F是强凸函数,从而有
另一方面,F是利普希茨连续的,从而有
由(11)和(12)式得到
将(13)式代入(10)式中可以得到
由初始条件和算法Q-PSDSG的第二步,可以得到,对任意i=1,…,n和t≥0,‖zj(t+1)‖是有界的[2],从而‖zi(t+1)-z*‖有界,故令
在(14)式中同时除以
$\frac{{a\left( {t + 1} \right)}}{n}$ ,有将(15)式两边乘以t再对t递归求和,同时乘以
$\frac{2}{{\tau \left( {\tau - 1} \right)}}$ 可得利用F的凸性,有
结合(16)和(17)式即可得出结论.
注1 定理1表明F(Ẑi(τ))接近最优F(z*)的程度主要由利普希茨常数、步长、概率量化精度和
$\sum\limits_{t = 1}^{\tau - 1} {\left\| {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{z}}_j}\left( {t + 1} \right) - \mathit{\boldsymbol{\bar x}}\left( t \right)} \right\|} $ 所确定.引理2 若假设1和假设2成立,则对于算法中的序列{zi(t)},i=1,…,n和时间τ≥1有:
其中:常数δ≥0,λ∈(0,1),D>0满足
$\delta \ge \frac{1}{{{n^{nB}}}}$ ,$\lambda \le {\left( {1 - \frac{1}{{{n^{nB}}}}} \right)^{\frac{1}{B}}}$ .引理2的证明类似于文献[2]中引理1的证明.同时,在引理2的条件下还可以得到:
定理2 在定理1的条件下,特别取α(t)=
$\frac{p}{t}$ ,t≥1,其中常数p满足则对每一个i有
这里
证 将α(t)=
$\frac{p}{t}$ 代入(14)式有两边同乘t(t+1),并对t递归求和,可以得到
运用
$\mathop {\max }\limits_i \left\| {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{z}}_i}\left( {t + 1} \right) - {\mathit{\boldsymbol{z}}^*}} \right\| = R$ 后,约去$\frac{p}{n}$ 再除以τ(τ-1)即得:因为F为凸函数,则有
结合(20)式和引理2即可推导出
简化处理(21)式以后定理2得证.
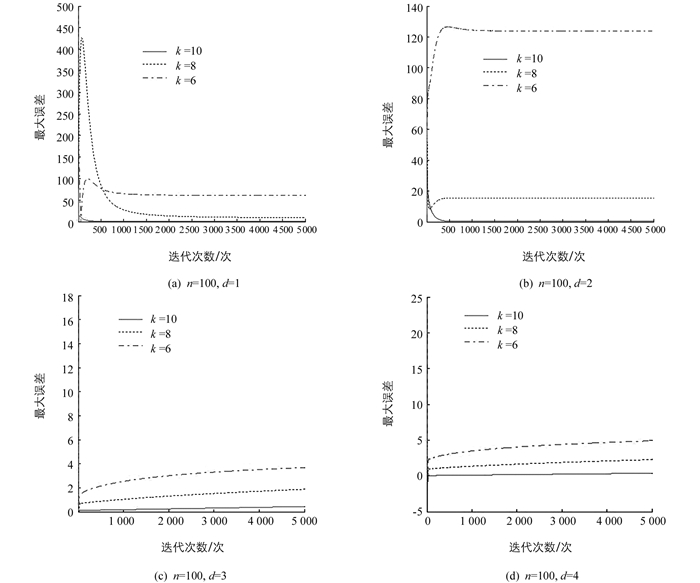
注2 由定理2可以看出,不等式(19)的前3项是优化误差项,后3项是量化误差项.当迭代次数τ趋于无穷时,优化误差项趋于零.对每个个体i,量化误差项
$\frac{1}{\Delta }{Q_1} + \frac{{\ln \tau }}{\Delta }{Q_2} + \frac{\tau }{{{\Delta ^2}}}{Q_3}$ ,取决于量化精度$\frac{1}{\Delta }$ 和常数Q1,Q2,Q3,故当量化精度足够高,即$\frac{1}{\Delta }$ →0时,定理2中量化误差项也趋于零,从而F(Ẑi(τ))接近最优F(z*).
-
本文研究了在有向网络下的带确定型量化的分布式push-sum次梯度算法,讨论了确定型量化对算法的收敛性影响.数值实验表明量化精度越高,越接近最优.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: