-
考虑下列不可压缩的Stokes问题
其中:有界区域
$ \mathit{\Omega} \subset {{\mathbb{R}}^{2}}$ 具有Lipschitz连续边界$\partial \mathit{\Omega} $ ,$ \mathit{\Gamma} \cap S=\varnothing , \overline{\mathit{\Gamma} \cup S}=\partial \mathit{\Omega} $ ;标量函数g≥0是阈值滑移函数;$ u_{n}=\boldsymbol{u} \cdot \boldsymbol{n}, u_{\tau}=\boldsymbol{u} \cdot \boldsymbol{\tau}$ 是速度在S上的法向分量和切向分量;$ \sigma_{\tau}=\boldsymbol{\sigma} \cdot \boldsymbol{\tau}$ 是Cauchy压力张量σ的切向分量,满足$ \sigma_{i}=\sigma_{i}(\boldsymbol{u}, p)=\left(v e_{i j}(\boldsymbol{u})-p \delta_{i j}\right) n_{j}$ ,其中$ e_{i j}(\boldsymbol{u})=\frac{\partial u_{i}}{\partial x^{j}}+\frac{\partial u_{j}}{\partial x^{i}}, i, j=1, 2$ ,当i=j时,δij=1,当i≠j时,δij=0.令$\psi: \mathbb{R} \longmapsto \overline{\mathbb{R}}=(-\infty, +\infty] $ 是一个具有凸性和弱下半连续性的函数(ψ与+∞不等),次微分集$ \partial \psi(a)$ 表示函数ψ在点a处的次微分:$ \partial \psi(a)=\{b \in \mathbb{R}: \psi(h)-\psi(a) \geqslant b(h-a), \forall h \in \mathbb{R}\}$ .带非线性滑移边界条件[1]的方程被应用于动脉硬化患者的血液流动、水和岩石的雪崩等模型中.在对Stokes方程进行数值模拟时,有限元是一种有效的方法[2-4].并行有限元算法由文献[5]提出,并被广泛应用与推广[6-10].本文在完全区域分解法[11]的基础上,设计了求解带非线性滑移边界条件的Stokes方程的一种并行有限元离散方法,其主要思想为在整个求解区域上定义多尺度网格(多尺度网格由所负责的子区域的细网格元素和覆盖余下区域的粗网格元素组成),并在多尺度网格上求解一个全局问题,获得给定子区域的近似解.
HTML
-
空间
$H^{k}(\mathit{\Omega})^{2} $ 的范数表示为$\|\cdot\|_{k}, L^{2}(\mathit{\Omega})^{2} $ 的内积与范数表示为(·,·)和‖·‖.本文所使用的空间为:空间V的内积与范数表示为
$(\nabla \cdot , \nabla \cdot ) $ 和$\|\cdot\|_{V}=\|\nabla \cdot\| $ ,定义:$ a(\boldsymbol{u}, \boldsymbol{v})=v(\nabla \boldsymbol{u}, \nabla \boldsymbol{v}), d(\boldsymbol{v}, q)=$ $(\nabla \cdot \boldsymbol{v}, q), \forall \boldsymbol{u}, \boldsymbol{v} \in V, q \in M $ .本文定义字母c为一个大于0的常数,它与网格参数无关,在不同式子可代表不同值.方程(1)的变分形式[12]为:求
$(\boldsymbol{u}, p) \in V \times M $ ,使得其中
$ j(\zeta)=\int_{S} g|\zeta| \boldsymbol{d} s, \zeta \in H^{\frac{1}{2}}(S)$ .方程(2)等价于以下变分等式[13]:求$(\boldsymbol{u}, p) \in V \times M $ ,存在且仅存在一个λ∈Λ,使得其中凸集Λ满足:
$\mathit{\Lambda}=\left\{\mu \in L^{2}(S), |\mu(x)| \leqslant 1, a, e, \text { on } S\right\} $ .假设对Ω的粗网格剖分TH和细网格剖分
$ T^{h}(0 <h <H <1)$ 都是拟一致剖分,速度和压力的有限元空间分别为$ V_{H}(\mathit{\Omega}) \subset V_{h}(\mathit{\Omega}) \subset V, M_{H}(\mathit{\Omega}) \subset M_{h}(\mathit{\Omega}) \subset M$ .若给定$ G \subset \mathit{\Omega} $ ,对于剖分Th,定义$ {{T}^{h}}(\mathit{\Omega}), {{V}_{h}}(\mathit{\Omega} ), {{M}_{h}}(\mathit{\Omega} )$ 在G上的限制为$T^{h}(G), V_{h}(G), M_{h}(G) $ ,且$ V_{0}^{h}(G)=\left\{\boldsymbol{v} \in V_{h}(G): \operatorname{supp} \boldsymbol{v} \subset \subset G\right\}$ ,$M_{0}^{h}(G)=\left\{q \in M_{h}(G): \operatorname{supp} q \subset \subset G\right\} $ .在混合空间的基本假设[6]条件下,方程(3)的有限元逼近如下:求$\left(\boldsymbol{u}_{h}, p_{h}\right) \in V \times M $ ,使得应用插值逼近定理[14],有以下结果
-
设
$ {{T}^{H}}(\mathit{\Omega} )$ 是网格尺寸为$H\gg h $ 的粗网格,$T^{h}\left(\mathit{\Omega}_{0}\right) $ 是局部细网格,其中Ω0是由子区域D向外扩展一定尺寸得到的(即$D \subset \subset \mathit{\Omega}_{0} \subset \mathit{\Omega} $ ).全局多尺度网格${{T}^{H, h}}(\mathit{\Omega} ) $ 表示对子区域Ω0生成尺寸为h的细网格,对其余区域生成尺寸为H的粗网格,它可以通过对整个区域的初始粗网格$ {{T}^{H}}(\mathit{\Omega} )$ 进行局部加密并通过自适应相容(即两单元交集或为空,或为一公共顶点,或为一公共边)得到.定义对应的有限元空间$ V_{H, h}(\mathit{\Omega}) \subset V$ ,$ {{M}_{H, h}}(\mathit{\Omega} )\subset M$ ,满足混合空间基本假设.因为子区域D包含多尺度网格$ {{T}^{H, h}}(\mathit{\Omega} )$ 的绝大多数自由度,故当我们使用$ {{T}^{H, h}}(\mathit{\Omega} )$ 解一个全局问题时,得到的是子区域D上的局部近似解.算法1 局部有限元算法
求
$ \left(\boldsymbol{u}_{H}^{h}, p_{H}^{h}\right) \in V_{H \cdot h}(\mathit{\Omega}) \times M_{H \cdot h}(\mathit{\Omega})$ ,使得引理1[15] 假设
$ \varphi \in H^{-1}(\mathit{\Omega})^{2}, D \subset \subset \mathit{\Omega}_{0} \subset \mathit{\Omega}$ ,对于$(\boldsymbol{w}, r)\in {{V}_{h}}(\mathit{\Omega} )\times {{M}_{h}}(\mathit{\Omega} ) $ ,满足且有以下局部误差估计
定理1 假设
$ \left(\boldsymbol{u}_{h}, p_{h}\right)$ 是方程(4)的标准有限元解,$\left(\boldsymbol{u}_{H}^{h}, p_{H}^{h}\right) $ 由算法1得到,满足则
证 由于
${{T}^{h}}(\mathit{\Omega} ) $ 与$ {{T}^{H, h}}(\mathit{\Omega} )$ 在Ω0上的假设一致,由方程(4)和算法1得到即
由引理1得到
结合(5)式、(6)式和(8)式,定理得证.
-
首先对求解区域Ω进行分解,得到互不重叠的子区域D1,D2,…,DJ,然后将Dj向外扩展一定尺寸得到相互重叠的子区域Ωj,满足
$ D_{j} \subset \subset \mathit{\Omega}_{j} \subset \mathit{\Omega}(j=1, 2, \cdots, J)$ .对于每一个Ωj,我们通过对初始粗网格$ {{T}^{H}}(\mathit{\Omega} )$ 进行局部改进和自适应过程得到多尺度网格$ T_{j}^{H, h}(\mathit{\Omega})$ ,它由Ωj区域的细网格元素和覆盖余下区域的粗网格元素组成.所有这些$ T_{j}^{H, h}(\mathit{\Omega})$ (j=1,2,…,J)就是对求解区域Ω的一个完全区域分解.并行有限元算法的基本思想就是在每个$ T_{j}^{H, h}(\mathit{\Omega})$ 并行地使用局部有限元算法,获得每个子区域Dj上的局部近似解.网格$ T_{j}^{H, h}(\mathit{\Omega})$ 所对应的有限元空间记为$V_{j}^{H, h}(\mathit{\Omega} )\subset V, M_{j}^{H, h}(\mathit{\Omega} )\subset M $ .算法2 并行有限元算法
1) 并行求
$\left( \boldsymbol{u}_{j}^{H, h}, p_{j}^{H, h} \right)\in V_{j}^{H, h}(\mathit{\Omega} )\times M_{j}^{H, h}(\mathit{\Omega} )(j=1, 2, \cdots , J) $ ,满足2) 在Dj中,取
$ \left( {{\boldsymbol{u}}^{h}}, {{p}^{h}} \right)=\left( \boldsymbol{u}_{j}^{H, h}, p_{j}^{H, h} \right)(j=1, 2, \cdots , J)$ .为进行并行有限元算法的误差分析,定义分片范数如下:
定理2 设
$ \left(\boldsymbol{u}^{h}, {p}^{h}\right)$ 是由算法2得到的近似解,满足则
证 由定理1得
对所有子区域Dj(j=1,2,…,J)上的结果求和,可得(10)式,再结合(5)式,定理得证.
-
本节中将给出数值算例以验证并行算法的有效性.数值实验所使用的计算机处理器为Inter(R) Core(TM)i3-2350M CPU 2.30 GHz,内存为4 GB.对每个多尺度网格
$ T_{j}^{H, h}(\mathit{\Omega})$ ,通过Uzawa迭代[13]解方程(9),得到子区域Ωj上的近似解$ \left( {{\boldsymbol{e}}_{j}}, {{\eta }_{j}} \right)$ .给定一个初始值λ0∈Λ,则λn为已知,我们通过以下式子求解$ \left( \boldsymbol{e}_{j}^{n}, \eta _{j}^{n} \right)$ 和${{\lambda }^{n+1}}(n=1, 2, 3\cdots ) $ :和
其中:参数
$ \rho>0, P_{A}: L^{2}(S) \longrightarrow \mathit{\Lambda}$ ,满足$ P_{\mathit{\Lambda}}(\gamma)=\sup (-1, \inf (1, \gamma)), \forall \gamma \in L^{2}(S)$ .通过Uzawa迭代法求解时,其迭代收敛标准为$\frac{\left\|\boldsymbol{e}_{j}^{n+1}-\boldsymbol{e}_{j}^{n}\right\|_{0 , \mathit{\Omega}}}{\left\|\boldsymbol{e}_{j}^{n+1}\right\|_{0, \mathit{\Omega}}} <10^{-6} $ ,其中${\mathit{\boldsymbol{e}}_j^n} $ 是第n次迭代解. -
考虑求解区域Ω=[0, 1]×[0, 1],其边界包含Γ和S两个部分:
准确解为
容易验证,准确解u满足:在Γ上,u =0;在S1上,
$\boldsymbol{u} \cdot \boldsymbol{n}=u_{1}=0, u_{2} \neq 0 $ 以及在S2上,u1≠0,$ \boldsymbol{u} \cdot \boldsymbol{n}=u_{2}=0$ ,切向单位向量τ在S1,S2上分别为(0,1),(-1,0),则另一方面,在S=S1∪S2上有|στ|≤g,则标量函数g在S1和S2上可取为g=-στ≥0.为考察算法的渐进误差,将求解区域分解成互不重叠的4个子区域:
然后将每个子区域Dj向外扩展尺寸h得到Ωj(j=1,2,3,4).计算时,取υ=0.01,迭代初值λ0=1,参数ρ=υ,使用P1b-P1元.算法2中细网格尺寸为
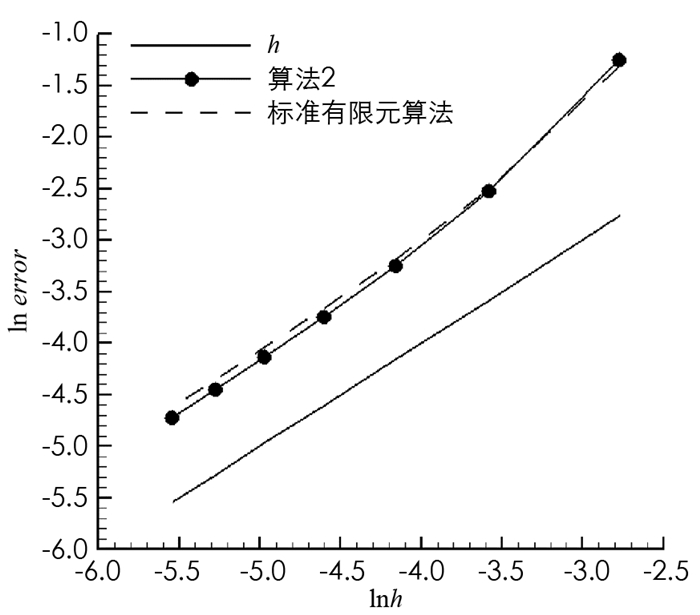
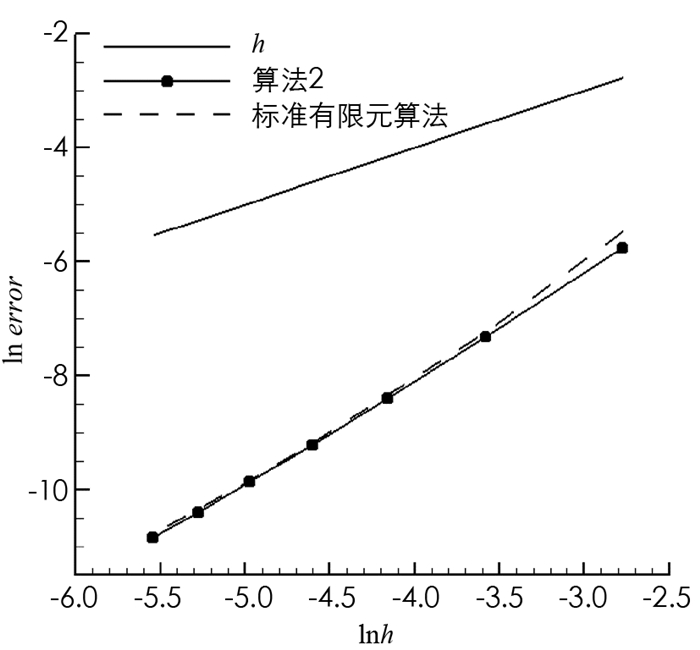
$h=\frac{1}{n^{2}}(n=4, 6, \cdots, 16) $ ,粗网格与细网格尺寸关系满足$2 H=h^{\frac{1}{2}} $ .表 1为标准有限元算法的数值结果,表 2为算法2的数值结果,其中,T为算法在4个子区域上计算时间的最大值,计算时间为网格生成时间、方程求解时间和误差计算时间之和. RuH1和RpL2分别表示相对误差$\frac{\left\|\boldsymbol{u}-\boldsymbol{u}_{h}\right\|_{1, \mathit{\Omega}}}{\|\boldsymbol{u}\|_{1, \mathit{\Omega}}} $ 和$\frac{\left\|p-p_{h}\right\|_{0, \mathit{\Omega}}}{\|p\|_{0, \mathit{\Omega}}} $ 关于h的收敛率.对比表 1和表 2可知,算法2与标准有限元算法的收敛阶(如图 1,2)和近似解精度没有明显差别,但对比T可以看出算法2能节省大量的计算时间. -
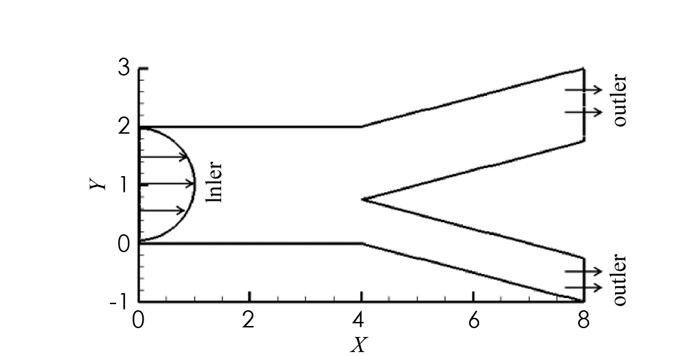
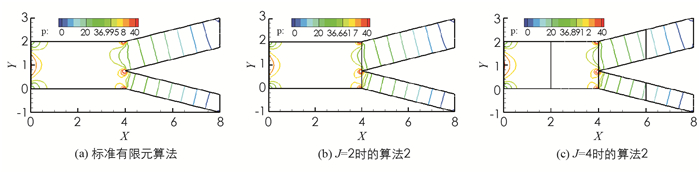
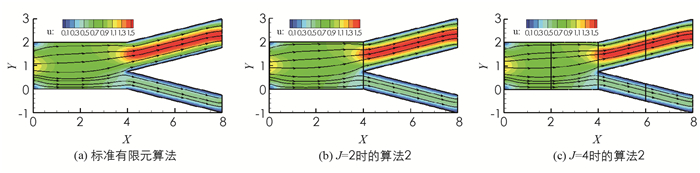
该算例研究了分叉动脉血管中血液流动的二维简化模型,假设血管为具有一定长度的“Y”字形管(图 3),血液从左入口流入主血管再从两个分支血管流出,流入速度为u1=1.2-1.2(y-1)2,u2=0.设主血管的直径为2,主分支出口的宽度为1.25,另一个分支出口的宽度为0.75,在主血管的上、下边界取滑移边界,阈值函数g=|στ|,其余的区域边界取Dirichlet边界.计算时使用P2-P1元,υ=1,应用Delaunay网格生成方法,细网格区域为每单位12个网格点,粗网格区域为每单位4个网格点.图 4-5分别为压力等值线、速度与流线的数值模拟图.图 4-5中,3组结果没有明显差别,压力在分叉连接处变化剧烈,速度在主分支血管内变化较大,并达到最大值.
4.1. 已知解析解
4.2. 分叉血液流动模型
-
基于完全区域分解法,本文设计并分析了一种求解带非线性滑移边界条件Stokes方程的并行有限元算法.通过数值算例,对比标准有限元算法,验证了并行有限元算法的有效性和高效性.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: